How to Meet Level 3 EV Charger Power Requirements in Commercial Spaces
Installing Level 3 EV chargers in commercial spaces is a strategic move toward accommodating the growing number of electric vehicle users. However, it requires careful planning and consideration of several technical aspects to ensure that the installation is both feasible and effective. Here’s a detailed look at how to meet the power requirements of these high-speed chargers:
1. Understanding Level 3 EV Charger Power Requirements
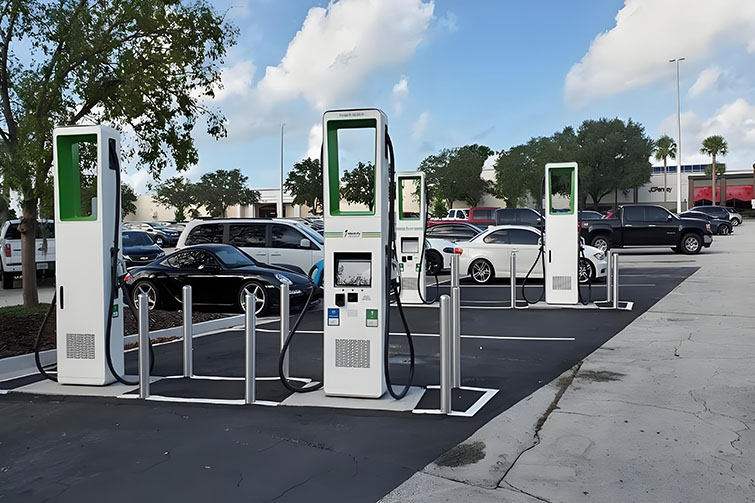
Level 3 EV chargers, also known as DC fast chargers, require significant power to operate. Typically, these chargers can deliver a voltage range from 200 to 1000 volts, with the power output ranging from 50 kW to 350 kW. This high level of power allows for rapid charging of EV batteries, significantly reducing waiting times compared to Level 1 and Level 2 chargers.
2. Assessing Infrastructure Needs
To accommodate a Level 3 charger, commercial facilities must have access to a high-capacity power source. This often means upgrading existing electrical infrastructure to handle the increased load. Key components of this upgrade include transformers, switchgear, and the possible integration of energy management systems to optimize power usage.
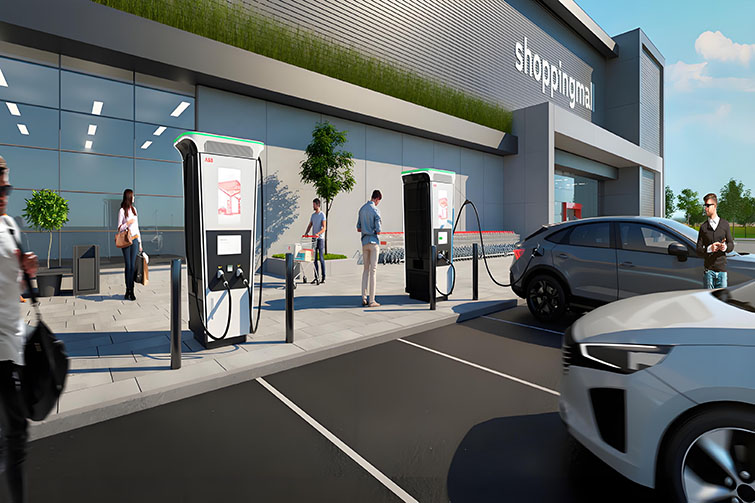

3. Level 3 Charger Voltage and Capacity
The voltage and capacity requirements for a Level 3 charger are considerably higher than those for slower chargers. A typical Level 3 charger operates at around 400 to 900 volts and can deliver 150 kW or more, which requires a robust electrical system to manage such high voltages safely.
4. Installation Considerations
Installing Level 3 fast chargers in commercial spaces involves not only technical challenges but also regulatory and compliance issues. It is essential to comply with local electrical codes and standards, and in many cases, the installation will require a professional assessment and potentially the involvement of local utilities.
5. Cost Implications
While the upfront cost of installing Level 3 chargers can be high due to the need for significant electrical upgrades and specialized equipment, the long-term benefits include attracting more EV owners and providing a valuable service that enhances the commercial value of the property.
Conclusion
Meeting the power requirements of Level 3 EV chargers in commercial spaces involves understanding the technical specifications and infrastructure needs. With careful planning and consideration of the voltage, kW capacity, and safety measures, commercial property owners can effectively integrate these chargers into their facilities. Doing so not only supports the adoption of electric vehicles but also positions the property as forward-thinking and customer-focused.